Executive Summary: HSA Translation Compliance 2026
- Regulatory Requirement: Translation is mandatory for Class B, C, and D medical devices under HSA GN-13 guidelines.
- Primary Risk: 23% of adverse drug events in Singapore’s elderly are linked to language barriers (Hokkien/Teochew vs. English/Mandarin).
- Legal Framework: Translation providers must act as Data Intermediaries under the PDPA, requiring AES-256 encryption and defined retention schedules.
- Key Success Factor: Shifting from literal translation to Transcreation for vernacular dialects to ensure patient adherence.
If you’re entering Singapore’s healthcare market in 2026, you’ll face a paradox. On one hand, the nation offers world‑class regulatory systems, an English‑trained medical workforce, and a healthcare sector racing ahead in innovation.
On the other hand, you face a demographic reality: by 2026, 21% of Singaporeans will be 65 or older This isn’t just a statistic for your market analysis deck; it’s the face of your primary consumer base for medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
Here's the problem: while your product documentation may be polished in English, the patients who will actually use your products often communicate in vernacular dialects, such as Hokkien, Teochew, and Cantonese. This disconnect creates what we call the “language rupture”: a safety‑critical gap where clinical excellence collides with communication failure.
Why Translation is Your First Market Entry Barrier
Many MedTech and Pharma companies treat translation as an administrative box to check. This is a mistake. In Singapore, translation is a clinical safety pillar.
If your Instructions for Use (IFU) are technically correct in English but culturally unintelligible to a 75-year-old patient, you risk:
- Medication non-compliance: Patients taking the wrong dose.
- Adverse events: Preventable hospital readmissions.
- Regulatory rejection: The HSA rejected your submission for lack of clarity.
The Reality Check: Translation isn’t overhead. It is the foundation of patient trust and market adoption.
Expert Healthcare Translation Services in Singapore for the Medical Sector

Expert healthcare translation services are specialized language solutions that convert medical documents, regulatory submissions, and patient communications into Singapore's required languages while maintaining clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, and cultural appropriateness.
In the Singapore medical sector, translation is not a "back-office" administrative task; it is a clinical safety pillar. While general translation focuses on fluency, healthcare translation focuses on error-free outcomes.
In 2026, a single mistranslated dosage instruction or a poorly localized contraindication doesn't just result in a typo; it can lead to a regulatory rejection or a patient adverse event.
Beyond Words: Managing Clinical Risk
To succeed in Singapore, your translation partner needs to operate on three levels simultaneously:
- Pharmacological Precision: Distinguishing between "side effects" (expected) and "adverse reactions" (harmful) in local dialects.
- Regulatory Alignment: Using the specific "controlled vocabulary" recognized by the Health Sciences Authority (HSA).
- Legal Data Protection: Treating every document as sensitive health data under the PDPA.
The Cost of "Near-Miss" Translations
For a medical device or pharmaceutical firm, the difference between an "Expert" and a "Generalist" is often measured in Market Velocity:
- The Generalist Path: Literal translation → HSA RFI (Request for Information) → 3-month launch delay → Potential post-market recall.
- The Expert Path: Clinically validated transcreation → First-time HSA approval → Immediate market adoption among the Silver Generation.
What Are the Different Types of Healthcare Translation Services?
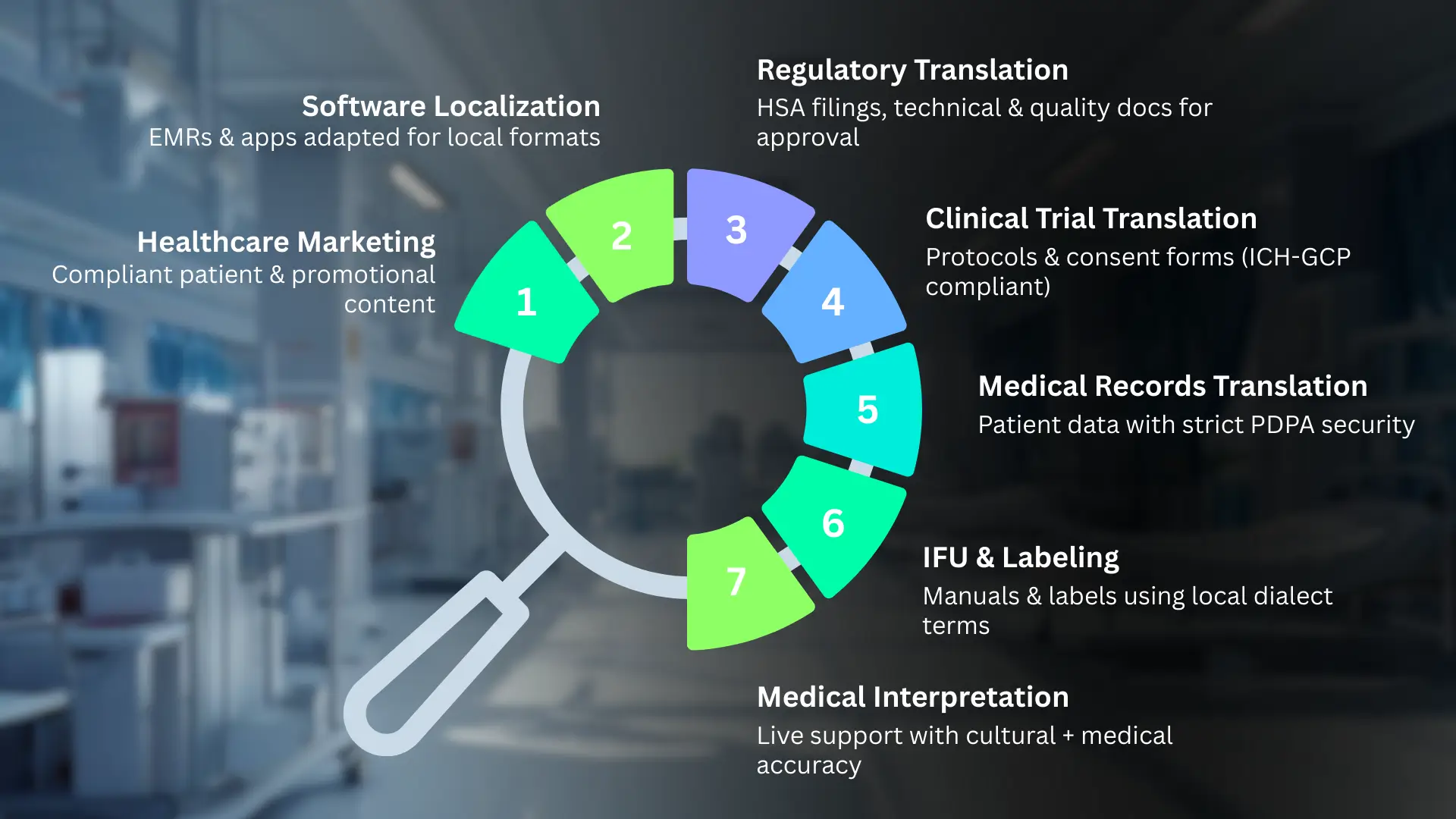
Medical translation services fall into seven categories based on your market entry needs and regulatory requirements.
- Regulatory Document Translation handles your HSA submissions, technical dossiers, clinical evaluation reports, and quality management documentation. These translations determine whether your device gets approved.
- Clinical Trial Translation covers protocols, informed consent forms, and adverse event reports. All clinical translations must meet ICH-GCP standards and Singapore's Human Biomedical Research Act requirements for ethics committee approval.
- Medical Record Translation processes patient histories, lab results, surgical notes, and discharge summaries. PDPA data protection rules apply strictly here; your translation provider needs documented encryption and deletion protocols.
- Instructions for Use (IFU) and Labeling include user manuals, warning labels, and packaging text. HSA requires these to use dialect-specific terms for elderly patients, not just standard Mandarin translations.
- Medical Interpretation provides real-time language support during consultations, telemedicine appointments, and informed consent discussions. Interpreters need both medical terminology knowledge and cultural understanding of health beliefs in Hokkien, Teochew, and Cantonese-speaking communities.
- Medical Software Localization adapts EMR systems, medical device interfaces, patient portals, and health apps. This goes beyond word translation to adjust date formats, measurement units, and cultural symbols for Singapore's multilingual environment.
- Healthcare Marketing Translation handles websites, patient education materials, conference presentations, and sales collateral while complying with Singapore's Health Products Act restrictions on health claims.
Which Healthcare Translation Services Do You Actually Need?
Medical translation isn't a monolith. Depending on your product lifecycle, you will need specific interventions.
| Service Type | Best For... | Critical Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Document Translation | HSA submissions, Technical Dossiers | Must match HSA GN-13/GN-15 terminologies. |
| Clinical Trial Translation | Informed Consent Forms (ICF), Protocols | Must meet ICH-GCP ethics standards. |
| Instructions for Use (IFU) | User manuals, Packaging | Dialect-specific terms for elderly safety. |
| Medical Interpretation | Telemedicine, Patient Consults | Cultural empathy (Hokkien/Cantonese). |
| Software Localization | EMR Systems, Health Apps | UI adaptation (Date formats, units). |
How to Prioritize services that your company needs?
Three factors determine your requirements:
- Your market entry stage dictates priorities: Pre-market companies need regulatory and clinical trial translation first. Post-market companies focus on patient materials and marketing content.
- Your product risk classification matters: Class C and D devices require a complete technical dossier translation. Lower-risk products may only need IFU and labeling.
- Your target patient age determines language needs: Products for elderly patients require dialect services. Products for younger patients may only need English and Mandarin.
Challenges in Healthcare Translation

Healthcare translation is one of the most demanding areas of professional language services. Unlike general content, medical documents carry life‑critical information where even the smallest error can have serious consequences.
- Complexity of Medical Terminology: Medical content is filled with specialized terminology, jargon, and directives. Translating these accurately requires deep subject‑matter expertise to ensure precise meanings are conveyed across multiple languages.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Healthcare communication must respect the beliefs, practices, and cultural nuances of diverse patient populations. A translation that overlooks cultural context can lead to misunderstandings or reduced patient trust.
- Legal & Regulatory Compliance: Translators must adhere to strict industry standards and guidelines. In Singapore, for example, compliance with the Health Sciences Authority (HSA) and alignment with global frameworks like ICH‑GCP are essential to ensure translations are legally recognized and accepted.
- Accuracy & Consistency: Consistency in terminology across medical records, insurance claims, and regulatory submissions is paramount. Any deviation can cause confusion, delay approvals, or compromise patient safety.
- Expertise & Experience: Overcoming these challenges demands not just linguistic skill but proven experience in healthcare and medical translation services. Partnering with certified providers ensures that translations meet both clinical and regulatory expectations.
Why Healthcare Translation Services Are Critical for Market Success
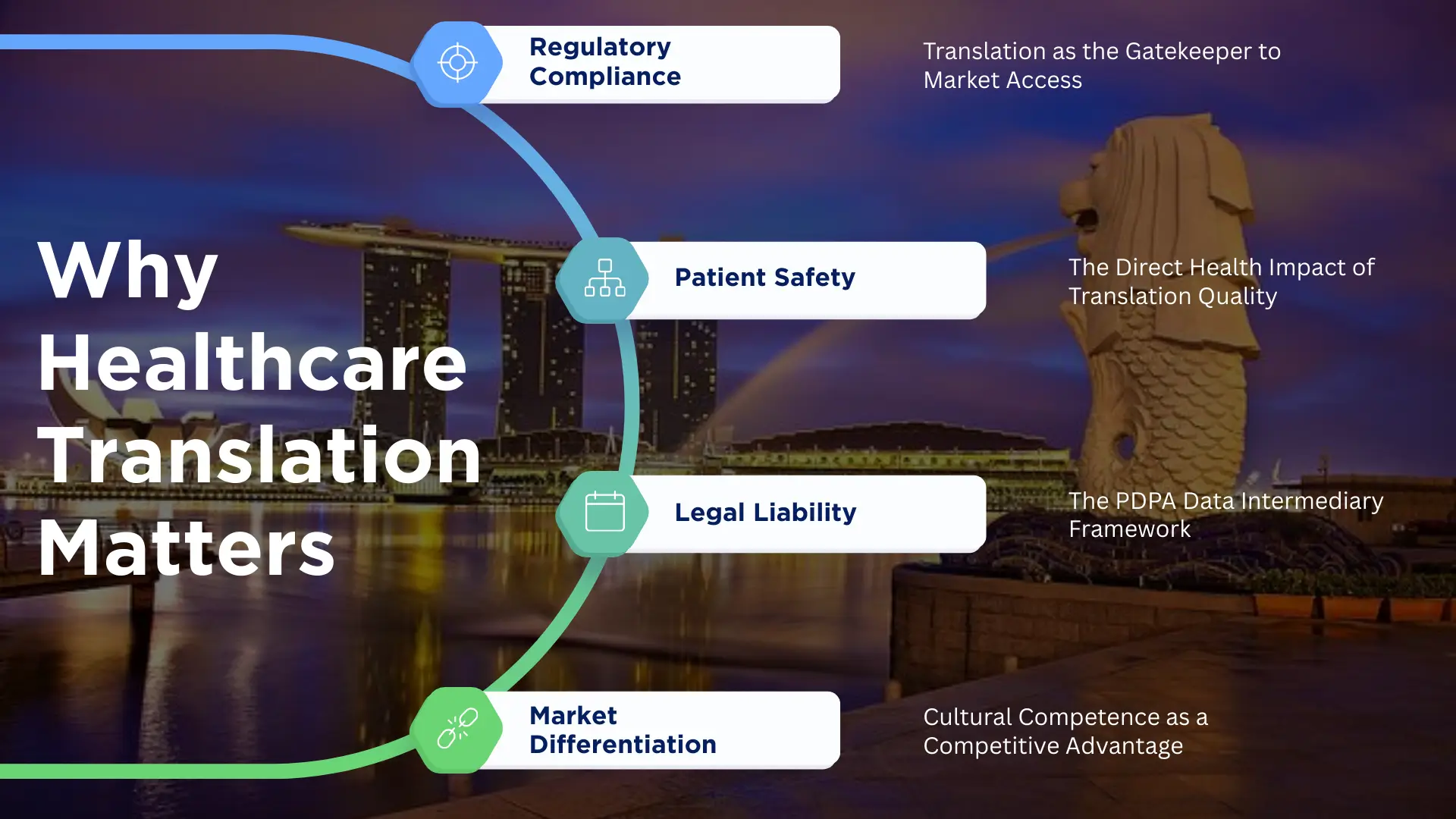
Regulatory Compliance: Translation as the Gatekeeper to Market Access
In Singapore, translation isn’t treated as optional localization; it’s a regulatory
requirement.
The Health Sciences Authority (HSA) directly links your translation strategy to your
approval
pathway and timeline.
Put simply: the quality of your translations can determine whether your medical device reaches the market quickly or faces costly delays.
HSA Regulatory Translation Requirements by Device Class
The Health Sciences Authority (HSA) links translation quality directly to the Product Registration timeline. Failure to provide localized Instructions for Use (IFU) is a common cause of "Request for Information" (RFI) delays.
| Device Class | Risk Level | Translation Requirement (GN-13/GN-15) | Validation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Low | English labels only (unless public-facing). | Self-Declaration |
| Class B | Low-Mod | Simplified IFU in English; Dialect support recommended for home-use. | Internal Audit |
| Class C/D | High | Full Technical Dossier + Patient Informed Consent Forms (ICF). | Back-Translation Mandatory |
The HSA mandates that technical dossiers, IFUs, and product labels must be localized, not just translated, for Singapore’s context.
Your Authorized Representative validates these translations during submission. Poor translation quality doesn’t just cause minor setbacks; it can delay approvals by quarters, not weeks.
Patient Safety: The Direct Health Impact of Translation Quality
In healthcare, translation errors aren’t just “quality issues”; they can cause real harm. When medical instructions are misunderstood, the consequences are immediate and measurable.
A 2019 study in Singapore’s public hospitals revealed that 23% of adverse drug events among elderly patients were linked to language barriers.
Put simply, when patients cannot read or understand their medication instructions, adherence drops by an average of 40%. That’s not a communication gap, it’s a safety crisis.
Legal Liability: The PDPA Data Intermediary Framework

When you handle medical translations in Singapore, you’re not just managing words; you’re managing sensitive patient data.
Under the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA), translation agencies working with clinical trial data, patient records, or informed consent forms are legally classified as “Data Intermediaries”.
This isn’t a minor detail; it’s a
Two Non‑Negotiable Obligations
-
Protection Obligation
Every piece of patient data must be safeguarded with industry‑grade security:- AES‑256 encryption as a minimum standard
- Role‑based access controls to prevent unauthorized handling
- Audit trails for full accountability
- Your translation partner should demonstrate compliance with ISO 27001 or SOC 2 Type II certifications to prove data protection is more than a promise.
-
Retention Limitation Obligation
Patient data cannot be stored indefinitely. Defined deletion protocols are mandatory:- Clinical trial translations require documented data destruction within 30 days of regulatory submission (unless otherwise specified).
- Clear retention timelines protect both sponsors and translation providers from compliance breaches.
The 2025/2026 Compliance Shift
Singapore’s PDPA framework is evolving. The shift from implied consent to express consent for sensitive medical data processing means your informed consent form translations must explicitly state:
- How translated versions will be stored
- Who will have access
- When and how they will be destroyed
Anything less than precise language creates legal exposure not only for sponsors but also for translation providers.
Market Differentiation: Cultural Competence as a Competitive Advantage

Singapore’s medical device market is among the most competitive in Asia, with over 1,200 registered manufacturers vying for patient adoption. In this crowded landscape, cultural competence is emerging as a clear differentiator.
Why Cultural Adaptation Matters
- Elderly adoption rates rise significantly when patient materials are localized.
- A 2024 Singapore study on older adults’ use of digital health services found that elderly patients aged 70+ were significantly more likely to adopt and correctly use medical devices and telehealth tools when instructions were provided in their preferred language (such as Mandarin, Malay, or dialects like Hokkien) rather than English only.
Beyond Translation
This isn’t simply about converting words from one language to another. It’s about:
- Respecting cultural identity → Patients feel seen and valued.
- Building trust → Seniors are more likely to comply with usage instructions.
- Driving outcomes → Higher adoption translates into stronger market share and better patient health results.
For manufacturers, cultural competence is more than a patient‑care initiative; it’s a market strategy. Devices that embed cultural respect into their design and communication are positioned to win in Singapore’s diverse healthcare ecosystem.
Choosing a Medical Translation Partner in Singapore: A Strategic Framework

Selecting a translation provider in the healthcare space isn't just a "vendor choice," it is a critical extension of your regulatory and safety infrastructure.
In a market as strictly regulated as Singapore, your choice of partner directly dictates your HSA approval speed, your liability exposure, and, ultimately, patient outcomes.
When vetting a partner, move beyond per-word pricing and evaluate these five pillars of high-stakes medical communication.
Regulatory "Teeth": Certification & HSA Alignment
Your provider's certifications are your first line of defense during a regulatory audit. You aren't just looking for someone who can speak the language; you need a partner who understands the Health Sciences Authority (HSA) ecosystem.
-
The "Big Three" Benchmarks: * ISO 17100: The gold standard for professional
translation workflows.
- ISO 9001: Proof of a systematic, repeatable approach to quality.
- ISO 13485: This is the deal-breaker for medical devices. It proves the vendor understands risk management and the life-cycle of medical documentation.
- HSA-Specific Validation: Not all "certified" translations are created equal. Ask your provider: “Have your translations successfully cleared HSA submissions for our specific device classification?”
The Data Privacy Mandate (PDPA & Beyond)
Medical translations often involve clinical trial data or patient-sensitive information. In Singapore, a breach isn't just a PR nightmare; it’s a massive legal liability under the PDPA.
- Security Infrastructure: Look for SOC 2 Type II or ISO 27001 certification. These aren't just badges; they ensure that the people handling your data have been vetted and that their servers are encrypted both at rest and in transit.
- The Audit Trail: Ask for their data destruction protocols. Once the project is over, how do they prove your sensitive clinical data has been purged? A professional partner provides a Certificate of Deletion.
Subject Matter Expertise: The "Med-Speak" Requirement
A generalist translator will fail in a clinical setting. To ensure patient safety, your translation team must possess a "Quad-Threat" of skills:
- Clinical Literacy: They should understand pharmacology and anatomy at a level comparable to a healthcare professional.
- Regulatory Fluency: They must be intimately familiar with HSA requirements, MDR, and FDA guidelines.
- Local Cultural Intelligence: As discussed, they must know how to pivot between formal Mandarin and the "street" dialects (Hokkien, Teochew) used by Singapore’s elderly.
- Technological Precision: They should be experts in medical databases like SNOMED CT and MedDRA to ensure every term used is globally standardized.
Quality Assurance: Beyond the First Draft
In medical translation, the "First Draft" is just the beginning. A robust Quality Management System (QMS) is what prevents a dosage error or a mislabeled contraindication.
- The Multi-Step Protocol: Your partner should follow a TEP (Translate, Edit, Proof) workflow, followed by Back-Translation for critical safety content. This "reverse-engineering" of the text is the only way to verify that the original clinical intent remains 100% intact.
- Terminology Assets: Ask how they maintain Translation Memories (TM) and client-specific glossaries. This ensures that "Brake" is translated consistently across your entire product line, saving you money on future updates and ensuring brand coherence.
The Reputation Stress Test
Finally, look at their track record. A provider can have all the right logos on their website, but their performance in the "regulatory trenches" matters most.
Don't just ask for references; ask for these specific metrics:
- What is their average turnaround for HSA-related clarification requests?
- How do they handle post-market support (e.g., translating adverse event reports on short notice)?
- Can they provide a reference from a company in your specific risk class (e.g., Class C or D medical devices)?
Choosing the Right Healthcare Translation Service Provider: The Decision Matrix
Rate each provider on a scale of 1–10 for each category. Multiply by the weight to get the total score.
| Evaluation Criteria | Weight | Provider A | Provider B | Provider C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSA Submission Success Rate (Proven track record of approvals) | 25% | |||
| ISO Certifications (Specifically 17100, 13485, and 27001) | 20% | |||
| Dialect & Cultural Intelligence (Hokkien, Teochew proficiency) | 15% | |||
| PDPA Compliance (Documented data security protocols) | 15% | |||
| Operational Velocity (Average project turnaround time) | 10% | |||
| Cost Efficiency (Price competitiveness vs. value) | 10% | |||
| Verified Peer References (From similar risk-class companies) | 5% | |||
| TOTAL WEIGHTED SCORE | 100% |
Score each provider on a 1-10 scale for each criterion, multiply by the weight, and sum the weighted scores. This removes subjective bias from procurement decisions and creates audit documentation for internal stakeholders.
Red Flags to Avoid:
Providers who cannot provide documented HSA submission examples, offer "rush" medical translations with turnaround times under 24 hours for complex documents, use only machine translation without human medical expert review, cannot demonstrate PDPA data handling procedures, or provide vague answers about translator qualifications and quality assurance processes.
If a provider cannot clearly articulate their quality process, they don't have one.
Expert Healthcare Translation Services Company in Singapore: LetterCrafts
LetterCrafts, a leading specialized medical translation service, plays a pivotal role in enabling multiple health insurance firms to navigate linguistic barriers effectively. We offer certified official translation services in Singapore, ensuring that translations are legally recognized and authenticated.
Why Healthcare Insurers Rely on LetterCrafts
- Specialized Medical Linguists: Every project is handled by translators with deep expertise in medical terminology, ensuring accuracy and compliance.
- Structured TEP Process: Translation → Editing → Proofreading, performed by native experts in Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Thai.
- Glossary Development: A validated glossary of medical terms was created with input from medical professionals, guaranteeing consistency across documents.
- Quality Control Tools: Automated QC systems catch errors early, reducing risk and improving reliability.
Our Specialized Regulatory Services
We provide end-to-end support for the entire product lifecycle:
- Market Entry: Technical dossier translation for HSA submissions and IMB (International Medical Device) filings.
- Clinical Trials: ICH-GCP compliant protocols, Informed Consent Forms (ICFs), and Investigator Brochures.
- Product Labeling: Localization of Instructions for Use (IFU) and risk management documentation (ISO 14971).
- Post-Market Safety: Vigilance reporting and post-market surveillance documentation.
Uncompromising Data Security & PDPA Compliance
We understand the sensitivity of clinical data. Our infrastructure is built to protect your intellectual property and patient privacy:
- Encryption: SOC 2 Type II certified handling with AES-256 encryption.
- Privacy: Full alignment with Singapore’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA), including 72-hour breach notification protocols and certified data destruction.
Partner with LetterCrafts for Market Entry Success
Operating in Singapore, LetterCrafts aligns with the region’s strict healthcare and insurance standards. Their certified translation services are legally recognized, giving insurers confidence that every submission meets regulatory expectations.
We don’t just translate words; we manage your regulatory risk. From the first clinical trial protocol to the final post-market report, LetterCrafts ensures your innovation reaches the patients who need it most.
Ready to streamline your HSA submission? [Contact Our Regulatory Specialists Today]
Conclusion

In Singapore’s tightly regulated healthcare and insurance landscape, translation is not just a linguistic task; it’s a compliance-critical function.
Whether you're submitting technical dossiers to the HSA, localizing clinical trial documentation, or translating insurance claims across Asian languages, accuracy, consistency, and cultural sensitivity are non-negotiable.
The strategic question isn't whether to invest in expert healthcare translation; it's whether you can afford the regulatory delays, legal exposure, and market penetration failures that come from treating translation as a procurement commodity rather than clinical infrastructure.
Contact LetterCrafts for a consultation on your Singapore market entry translation requirements. We provide detailed project scoping, HSA submission timeline analysis, and sample translations demonstrating our quality standards at no cost or obligation.