TL;DR: Manufacturing Translation in Singapore:
As Singapore targets its "Manufacturing 2030" goal (50% increase in value), technical translation has evolved from a "back-office task" to a critical legal and safety requirement In 2026, a single mistranslated warning is a massive liability.
3 Direct Takeaways for 2026:
- GHS Deadline Warning: The grace period for SS 586 (GHS 7th Edition) expired in February 2025. If your Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are not updated with localized pictograms, your exports face immediate rejection at Jurong Island and Tuas checkpoints.
- Safety = Logic, Not Just Words: Generic AI (like basic ChatGPT) lacks "physics awareness." A mistranslated torque setting or "Emergency Stop" UI command can cause equipment failure. You need who understand technical logic. cause equipment failure. You need Engineer-Linguists who understand technical logic.
- Translation Memory (TM) is Essential: Modern services use TM databases to "remember" technical phrases. You only pay for a sentence once, even if it appears in 100 manuals, ensuring both consistency and cost-efficiency.
The Conclusion: For 2026 compliance and global scaling, LetterCrafts is the top choice for its blend of engineering expertise and transparent pricing. Avoid generic agencies for technical work; precision is the only currency in Industry 4.0.
Manufacturing Translation in Singapore: The Hidden Engine of Industry 4.0
Singapore’s "Manufacturing 2030" initiative aims to boost manufacturing value by 50%. But as we
scale toward this goal, the industry faces a critical bottleneck that automation cannot solve:
The Language Gap
For companies operating in Tuas or exporting to the EU, a translation error isn't just a typo; it's a liability. Whether it is a jet engine manual or a chemical Safety Data Sheet (SDS) precision is the difference between a successful audit and a halted production line.
Why is Accurate Translation Critical
- Safety: A mistranslated warning can lead to real-world injury.
- Compliance: One error in a regulatory filing can shutter a production line for weeks.
- Liability: "Lost in translation" is a legal nightmare no manufacturer wants to navigate.
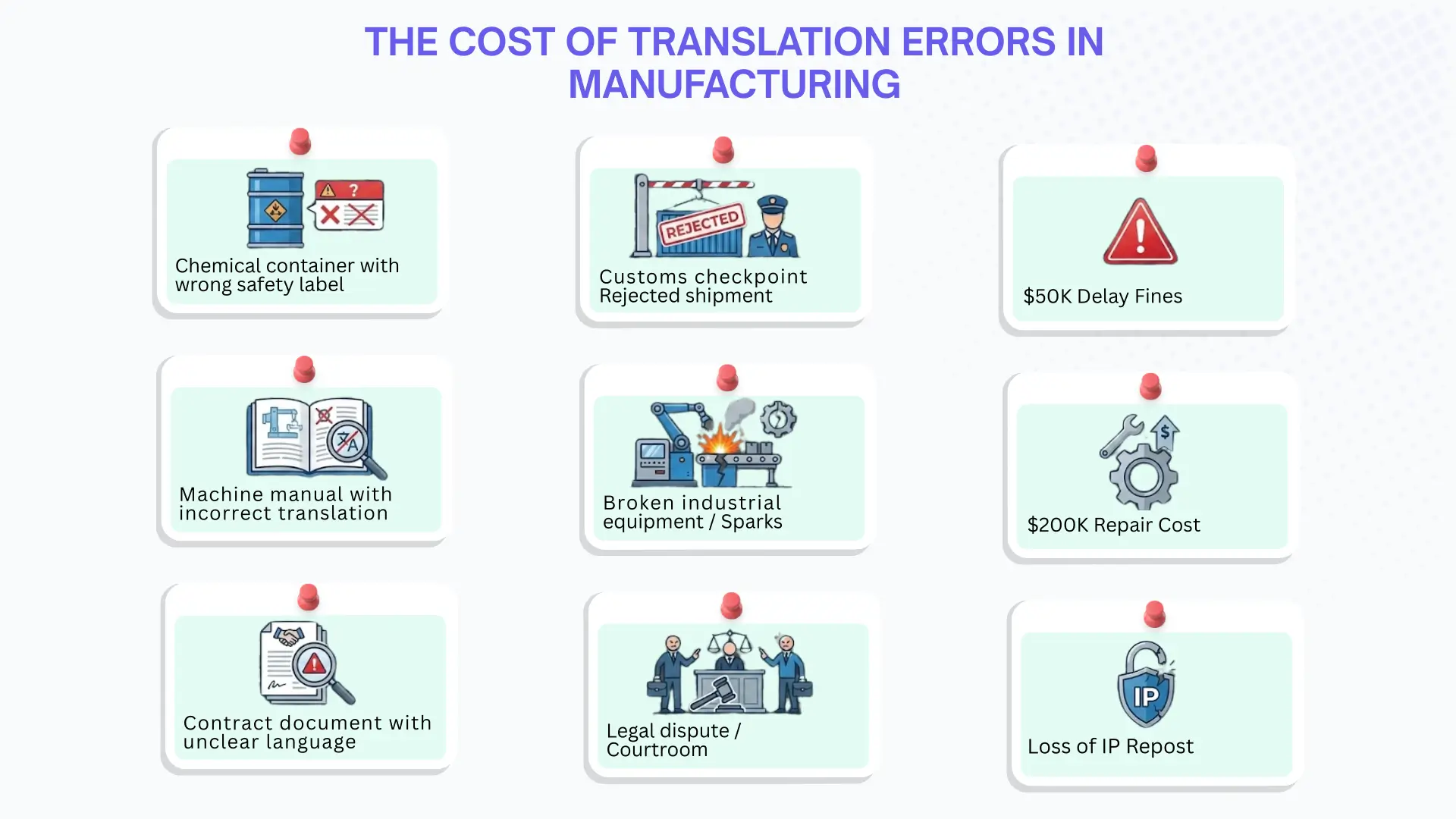
To thrive in this new era, it’s not enough to simply swap English words for Mandarin, German, or Malay. You have to localize the logic If your technical documentation can’t keep pace with the speed of your innovation, it becomes an anchor rather than an asset. To lead the market, your manuals and specs need to be as precise as the engineering they describe.
The Singapore Context: A Quad-Lingual Hub
Manufacturing translation is the technical conversion of industrial documentation such as CAD drawings, SDS, and SOPs, ensuring engineering accuracy and regulatory compliance (e.g., SS 586) across languages.
Unlike general translation, it requires subject matter expertise (SME) to distinguish between a "bus" (transport vehicle) and a "bus" (electrical conductor). A general translator uses a dictionary; a manufacturing translator uses engineering blueprints
Pillars of Manufacturing Translation in Singapore Pillar
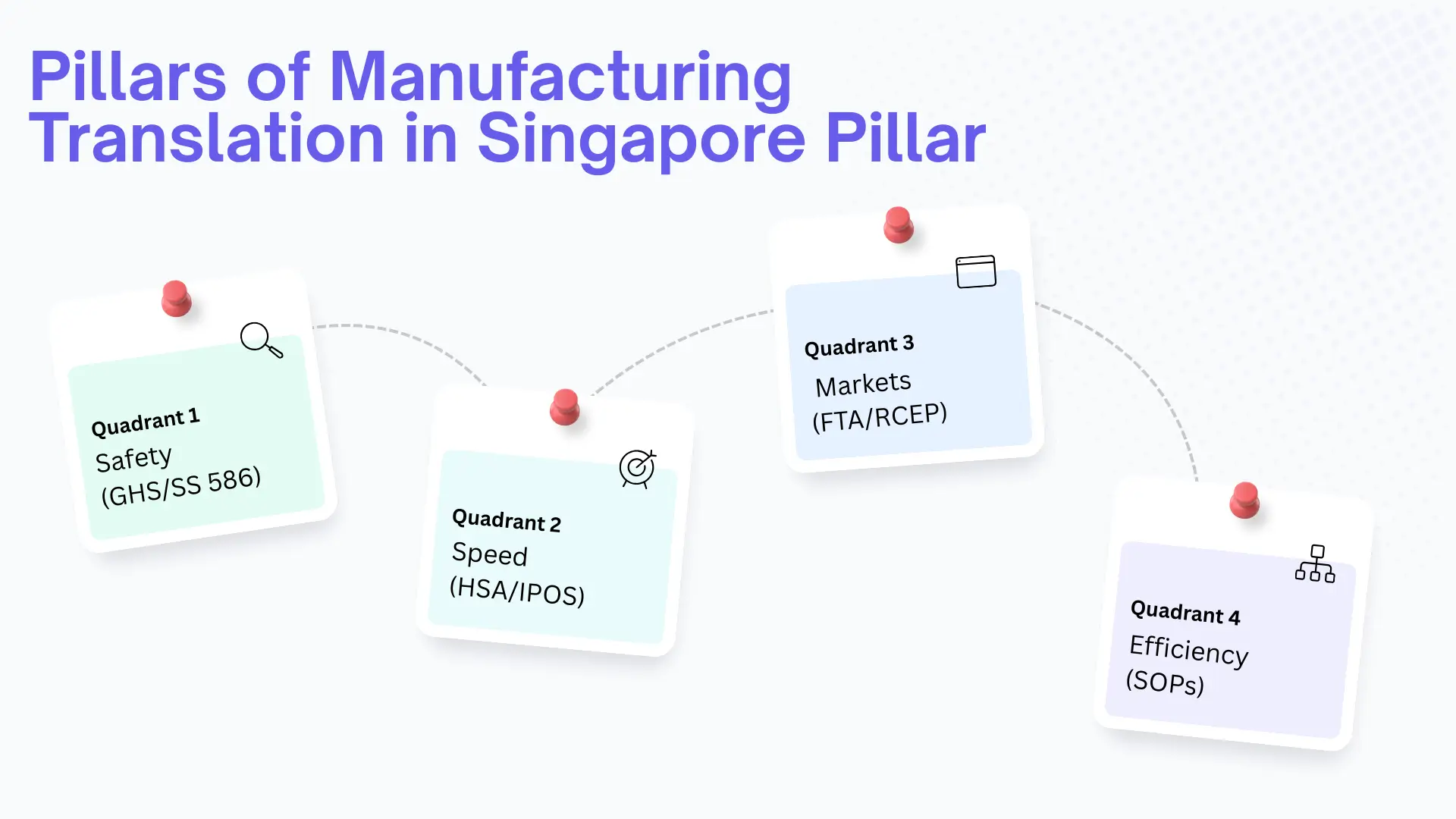
Safety & Liability (The Jurong Island Standard)
- Risk: A misinterpreted warning label on hazardous chemicals could result in injury and substantial penalties under the Workplace Safety and Health Act.
- The Regulation: As of 2026, compliance with SS 586 (GHS 7th Edition) is strictly enforced.
- The Solution: We localize Hazard Pictograms and Precautionary Statements to your needs, guaranteeing your Safety Data Sheets comply with NEA standards, thus avoiding any customs issues.
⚠️ Compliance Alert: As of February 2025, the grace period for GHS 7th Edition (SS 586) has expired. If your SDS and labels are still using 2024 terminology, your 2026 exports are at high risk of customs rejection and NEA fines.
Regulatory Speed (HSA & IPOS)
Singapore's Health Sciences Authority (HSA) and global bodies like the FDA reject submissions with ambiguous terminology. A single error can delay product launches by months.
Furthermore, protecting intellectual property is the first step in exporting. We offer accurate patent claim translations, serving the Intellectual Property Office of Singapore (IPOS) and various international bodies, such as WIPO.
Unlocking Global Markets via FTAs
Singapore's web of Free Trade Agreements, encompassing the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) and the EU-Singapore FTA (EUSFTA), provides a considerable edge in the global marketplace.
However, to utilize these benefits, your products must meet strict "Rules of Origin" and technical labeling standards in the destination country’s local language. Professional translation isn't just a cost; it is the key that unlocks tariff-free trade in Europe and the Asia-Pacific.
Operational Efficiency
Your workforce is multilingual. Technicians on the ground need clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) in their native languages (Malay, Mandarin, Tamil, and Vietnamese) to maintain efficiency and safety.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
| Document Category | Examples | Key Risk of Error |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Manuals | User Guides, Maintenance SOPs, CAD Drawings | Equipment failure, Operator injury |
| Compliance Docs | Safety Data Sheets (SDS), HSA Submissions, Patents | Fines, Product Recall, Customs Rejection |
| Marketing Materials | White Papers, Case Studies, Website Localization | Brand damage, Low conversion rates |
| Software/UI | Machine Interfaces (HMI), IoT Dashboards | Operational errors, User frustration |
In the world of advanced manufacturing, documentation is the "nervous system" of your operation. It’s what connects a designer’s intent in a lab to an operator’s action on the shop floor.
As we push toward the Manufacturing 2030 goals the complexity of these documents is skyrocketing. Here are the three critical categories where "basic translation" isn't enough; you need professional, technical precision.
Technical Documents: The Blueprints of Communication
Technical documents are the interface between your engineering team and your global workforce. If a technician in Jurong or a plant manager in Germany misinterprets a torque setting or a wiring diagram, the result is downtime or worse, equipment failure.
- User Manuals & Operating Procedures (SOPs): These are more than just "how-to" guides; they are your company’s gold standard for consistency. Professional translation ensures that the logic of the machine remains the same, regardless of the language the operator speaks.
- Maintenance & Repair Guides: It’s 2026 with Agentic AI and robotics becoming floor staples, maintenance isn't what it used to be. Localizing these guides perfectly means your local teams can troubleshoot in real-time, rather than waiting for a 12-hour time zone window to open up for a "help" call.
- Technical Specifications & CAD Drawings: In manufacturing, precision is the entire game. A mistranslated unit of measure or a misplaced decimal point doesn’t just cause a headache; it can scrap an entire production run before it even starts.
Marketing Materials: Expanding Reach with Trust
You aren't just selling a machine or a chemical; you're selling reliability. In a crowded global market, your marketing materials need to speak the language of the local industry expert, not just a dictionary.
- Case Studies & White Papers: These prove your value. Professional translators ensure your "innovative solutions" don't read like a word-for-word technical dump, but like a compelling business case.
- Trade show materials and pitch decks: First impressions are everything. Localization, sometimes referred to as transcreation, is vital. It guarantees your brand's voice stays strong and culturally relevant, no matter if you're presenting in Tokyo or Zurich.
- Digital Presence (Websites & Apps): With the rise of the digital economy in ASEAN, having a multilingual, SEO-optimized presence is the difference between being a "local secret" and a "global leader".
Product Labeling & Compliance: The Legal Shield
This is where translation moves from "business strategy" to "legal necessity." With Singapore’s new NEA mandatory hazardous substances reporting (effective January 2026), the margin for error has hit zero.
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS): Under the updated SS 586 (GHS 7th Edition) standards, your SDS must be linguistically and technically accurate. A mistranslated hazard statement isn't just a typo; it’s a non-compliance fine or a safety catastrophe.
- Product Labels & Warning Signs: These must meet local regulatory layouts and font requirements. One missing pictogram or a poorly translated warning can lead to a shipment being rejected at customs.
- Regulatory Submissions: For biotechnology and aerospace, submitting documents to regulatory bodies like the Health Sciences Authority (HSA) requires a high level of linguistic precision, which is best provided by someone with specific expertise in the subject.
What Are the Challenges of Translation and Localisation in Manufacturing?

Ideally, production and documentation would happen together. But in reality, when your documentation lags behind a fast-moving production line, it becomes the ultimate bottleneck for global scaling.
In the manufacturing context, translation is an engineering challenge with distinct hurdles:
- Terminology Inconsistency: A single component might be referred to as a "valve," "regulator," or "control" across different departments. Without a centralized glossary, these inconsistencies lead to confusion on the assembly line and non-compliance in audits.
- Space Constraints in User Interfaces (UI): For "Smart Manufacturing" and IoT devices, software localization is critical. German or French text often expands by 30% compared to English. If a translator does not understand the UI constraints of a machine’s control panel, critical "Emergency Stop" commands might be truncated or unintelligible.
- Format Preservation (DTP): Manufacturing documentation is rarely in simple Word documents. It exists in complex AutoCAD drawings, InDesign manuals, and XML files. Extracting text from a CAD drawing without breaking the design layers or corrupting the file requires specialized engineering software and know-how.
- The "Version Control" Nightmare: Engineering specs change frequently. When a manual is updated in English (v2.1), ensuring that the Malay, Vietnamese, and Thai versions are simultaneously updated without translating the entire document again is a massive logistical challenge.
Sector-Specific Precision: Where Accuracy Meets Engineering
Generic translation fails in manufacturing because every vertical has its own lexicon. Here is how we address Singapore's core pillars:
| Industry Sector | Critical Documentation | Compliance & Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Semiconductors | GUI Localization, Hardware Specs, IC Data Sheets | IEEE Standards, Rapid Time-to-Market (TTM) |
| Biomedical & MedTech | IFUs, Labelling, Clinical Trial Data | HSA GN-17/23, ISO 13485, CE Marking |
| Aerospace & MRO | AMM, SRM, Component Maintenance Manuals | AS9100, CAAS Requirements, Seletar Park Standards |
| Chemical & Energy | Safety Data Sheets (SDS), Plant SOPs | GHS, SS 586 (Singapore Standard) |
Professional Manufacturing Translation Services Company in Singapore: LetterCrafts
In an industry where precision is the only currency, LetterCrafts stands as the bridge between Singaporean engineering and the global market. Here is why leading manufacturers trust us:
- Subject Matter Expertise: We do not rely on generalists. Your chemical safety data sheets are handled by linguists with backgrounds in chemistry; your avionics manuals are translated by those who understand aerospace engineering. We match the domain expertise, not just the language pair.
- The Geometric Pricing Model: Traditional agencies charge per word, punishing you for volume. We utilize a unique Geometric Pricing Model combined with Translation Memory. We analyze your documents for repetitions. If a safety warning appears 50 times across your manuals, you only pay for it once.
- Data Security & IP Protection: We understand that your schematics and patent claims represent your company's edge. At LetterCrafts, we handle your data with the utmost care. Stringent NDAs and robust, banking-grade cybersecurity measures safeguard each project. This guarantees that your intellectual property remains precisely where it should be: under your control.
- Speed at Scale: With our "Follow the Sun" workflow, we can leverage time zones to deliver urgent compliance documents overnight, ensuring your product launch isn't delayed by paperwork.
Our Process: The "Engineer-Linguist" Difference
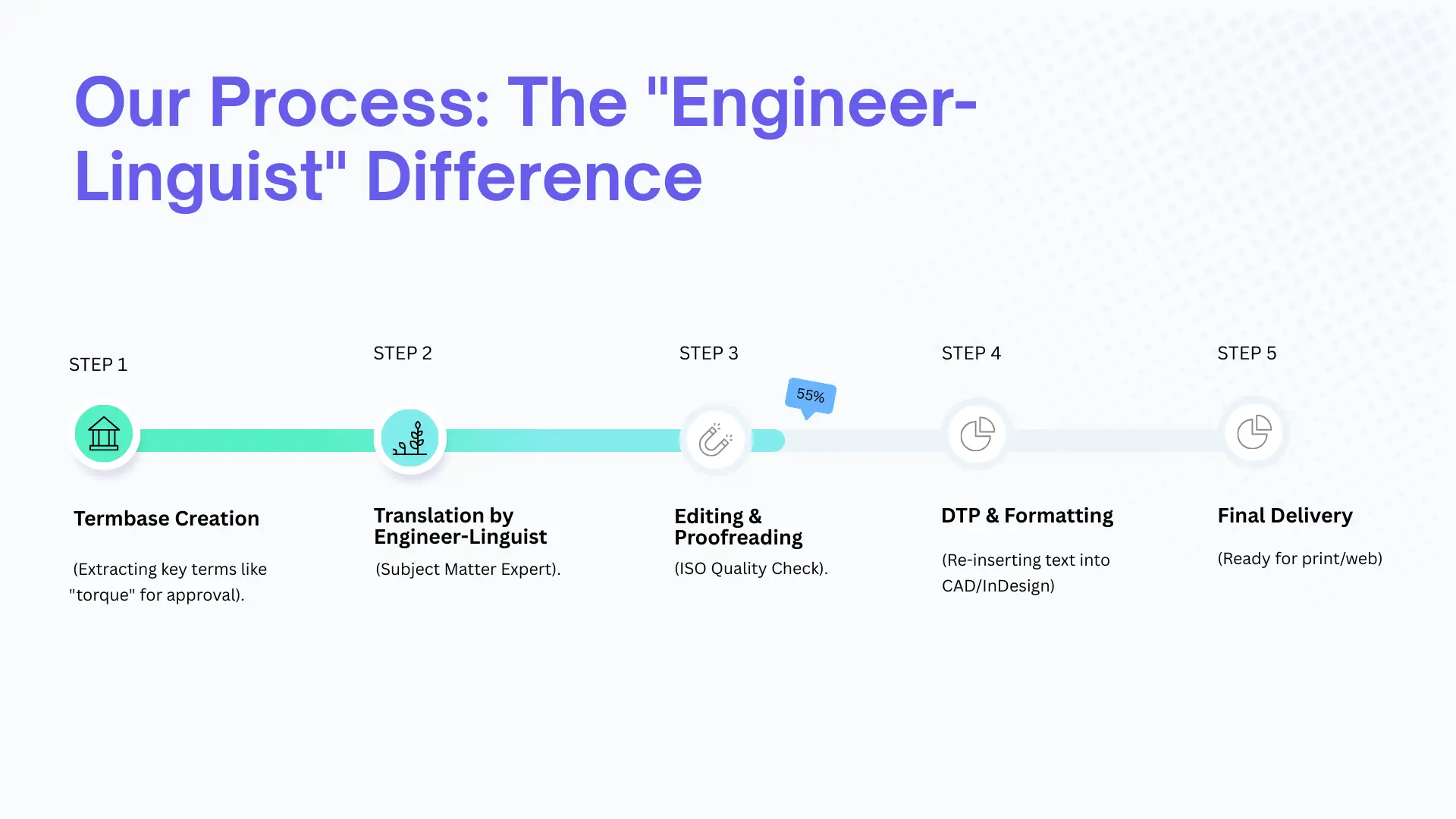
At LetterCrafts, we know that in technical fields, a small mistranslation can cause a massive headache. So that's why we use a rigorous TEP (Translation, Editing, Proofreading) workflow designed to catch even the smallest slip-ups.
- Content Analysis & Termbase Creation: Before we translate a single sentence, we dig into the nitty-gritty. We extract your specific technical terms like "torque" or "actuator" to build a glossary just for you. This ensures consistency from page one.
- Translation by Engineer-Linguists: This is where we stand apart. Most agencies use generalist translators who might see the word "driver" and think of a vehicle operator, when you actually meant software. We hire Engineer-Linguists
- The "Translation Memory" Advantage: Manufacturing content is highly repetitive. We use Translation Memory (TM) tools to store every translated sentence. If a sentence in your manual repeats, you pay for it once. This reduces costs by up to 40% for large technical manuals
- AI vs. Accuracy: Why Google Translate Isn't Safe for Engineering. Can you use AI for manufacturing translation?
No, not for compliance documents. While Neural Machine Translation (NMT) is fast, it lacks "physics awareness." AI might translate "pressure" as psychological stress rather than atmospheric force.
Our Hybrid Model: We use MTPE (Machine Translation Post-Editing). AI handles the volume, but human Engineer-Linguists verify the logic. This ensures you get AI speed with human safety guarantees.
Technical Manual Translation Cost in Singapore: Driving Value with Technology
When evaluating the technical manual translation cost in Singapore most manufacturers only look at the "per-word" rate. However, the true cost is determined by how much content can be reused. At LetterCrafts, we use Translation Memory (TM) technology to ensure you never pay for the same sentence twice.
How Translation Memory (TM) Reduces Your Costs
Translation Memory is a secure database that "remembers" every sentence we translate for you. When a phrase is repeated in technical manuals and SOPs, the system automatically suggests the previous translation.
Cost Breakdown Comparison:
| Factor | Standard Translation | With Translation Memory (TM) |
|---|---|---|
| Repeated Phrases | Charged at 100% rate | Charged at a 20-30% rate (or free) |
| Consistency | Risk of manual errors | 100% Guaranteed consistency |
| Turnaround Time | Slower (Manual) | Up to 40% Faster |
| Scalability | Costs increase linearly | Costs decrease as your database grows |
Pro Tip: For high-volume projects, like a 200-page aerospace manual, TM technology can reduce the total technical manual translation cost in Singapore by 30% to 50% over the project lifecycle.
Conclusion: Engineering Your Global Success

In the landscape of "Manufacturing 2030," linguistic precision is the silent engine that drives Singapore’s industrial competitiveness. As we have seen, the transition from a local facility to a global powerhouse is paved with documentation manuals that must be understood, safety protocols that must be followed, and regulatory filings that must be flawless.
Whether you are navigating the strictures of the HSA, submitting patents to IPOS, or exporting semiconductors to the EU, your translation quality is a direct reflection of your engineering quality. Choosing a partner like LetterCrafts ensures that your technical logic survives the language barrier, protecting your liability, your brand, and your bottom line.
Ready to Scale Your Production?
Don't let language barriers slow down your supply chain. Ensure your documentation is as high-performance as your machinery.